Zero Trust Security: Principles, Technologies & Implementation Guide
What Is Zero Trust Security?
This modern cybersecurity framework challenges the traditional notion of a trusted internal network. Operating on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” it has become essential for protecting data, systems, and users in today’s threat landscape. As organisations face increasingly sophisticated attacks, adopting a model that assumes no implicit trust is now a necessity.
Further reading:
The Origins of Zero Trust
The concept was introduced by John Kindervag at Forrester Research in 2010. It emerged as a response to the limitations of perimeter-based security, where firewalls and VPNs protected a supposedly safe internal network. With the rise of cloud services and mobile workforces, this approach became outdated, paving the way for a new model that treats every access request with scrutiny.
Learn more:
- How to Measure Zero Trust Maturity: Practical Steps, Common Gaps, and Implementation Guide
- What is NIST?
- Forrester: Zero Trust Security Business Benefits
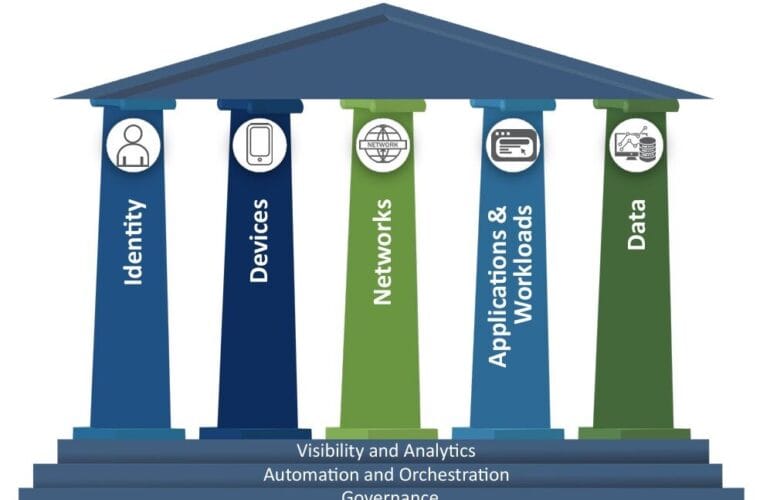
Core Principles
-
Never Trust, Always Verify:
Every access request—regardless of origin—must be authenticated, authorised, and continuously validated. -
Least Privilege Access:
Users and systems receive only the minimum access necessary, reducing the risk from compromised accounts. -
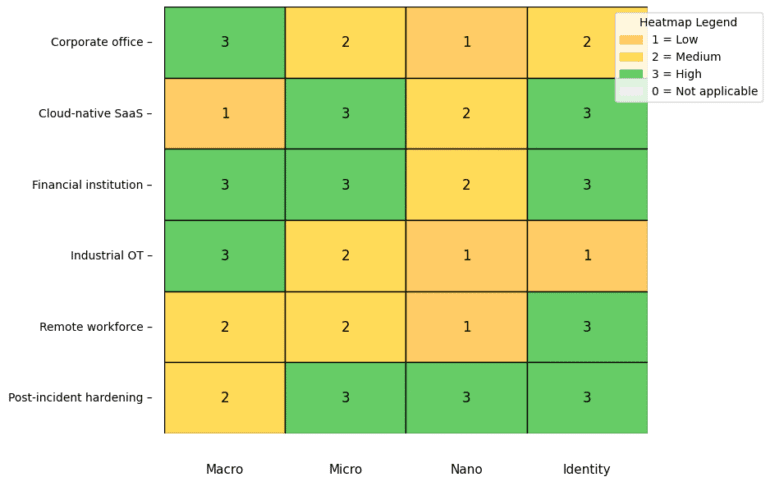
Micro-Segmentation:
Dividing networks into smaller zones limits lateral movement if a breach occurs. For example, segmenting sensitive data from general user areas can prevent attackers from moving freely.Further reading:
Effective Network Segmentation Strategies for Corporate Networks
Integrating Microsegmentation Successfully: 10 Key Considerations
Agent and Agentless Microsegmentation: A Comparison
Shifting Left with Microsegmentation in Your CI/CD Pipeline
Top Microsegmentation Vendors 2025: Comprehensive Comparison
NIST Zero Trust Architecture -
Assume Breach:
This approach operates under the assumption that breaches are inevitable, driving proactive monitoring and rapid response.Further reading:
Redefining the Network Security Perimeter in a Zero Trust World (2025 and Beyond) -
Continuous Monitoring and Analytics:
Security doesn’t end at login. Real-time monitoring of user behaviour, device health, and network activity helps detect anomalies and threats. For instance, analytics can flag unusual access patterns for investigation.Further reading:
5 Reasons Continuous Threat Exposure Management Matters Today
Zero Trust Guidance Center (Microsoft)
Why Organisations Are Adopting This Approach
The shift to remote work, cloud adoption, and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies has blurred the traditional network perimeter. A trust-based access model provides a robust solution for these challenges.
- Enhanced security posture
- Reduced attack surface
- Improved compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.)
- Greater visibility into user and device activity
- Faster breach detection and response
See also:
- Understanding Zero Trust Maturity Models: We Compare the 3 Main Approaches
- Zero Trust Maturity Model (CISA)
- Zero Trust Security: The Business Benefits (Forrester)
Technologies Enabling the Framework
Implementing this security model requires a combination of tools and practices, including:
- What is IAM? A Useful Guide
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB)
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Implementation guides:
- How To approach implementing Zero Trust?
- Advice – Prepare a Zero Trust Roadmap
- NIST SP 1800-35: Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture
- Zero Trust Implementation (NSA)
Real-World Use Cases
- Healthcare: Protecting patient data across cloud platforms and mobile devices.
- Finance: Securing transactions and customer information from insider threats.
- Government: Ensuring secure access to sensitive systems for remote workers and contractors.
Case studies:
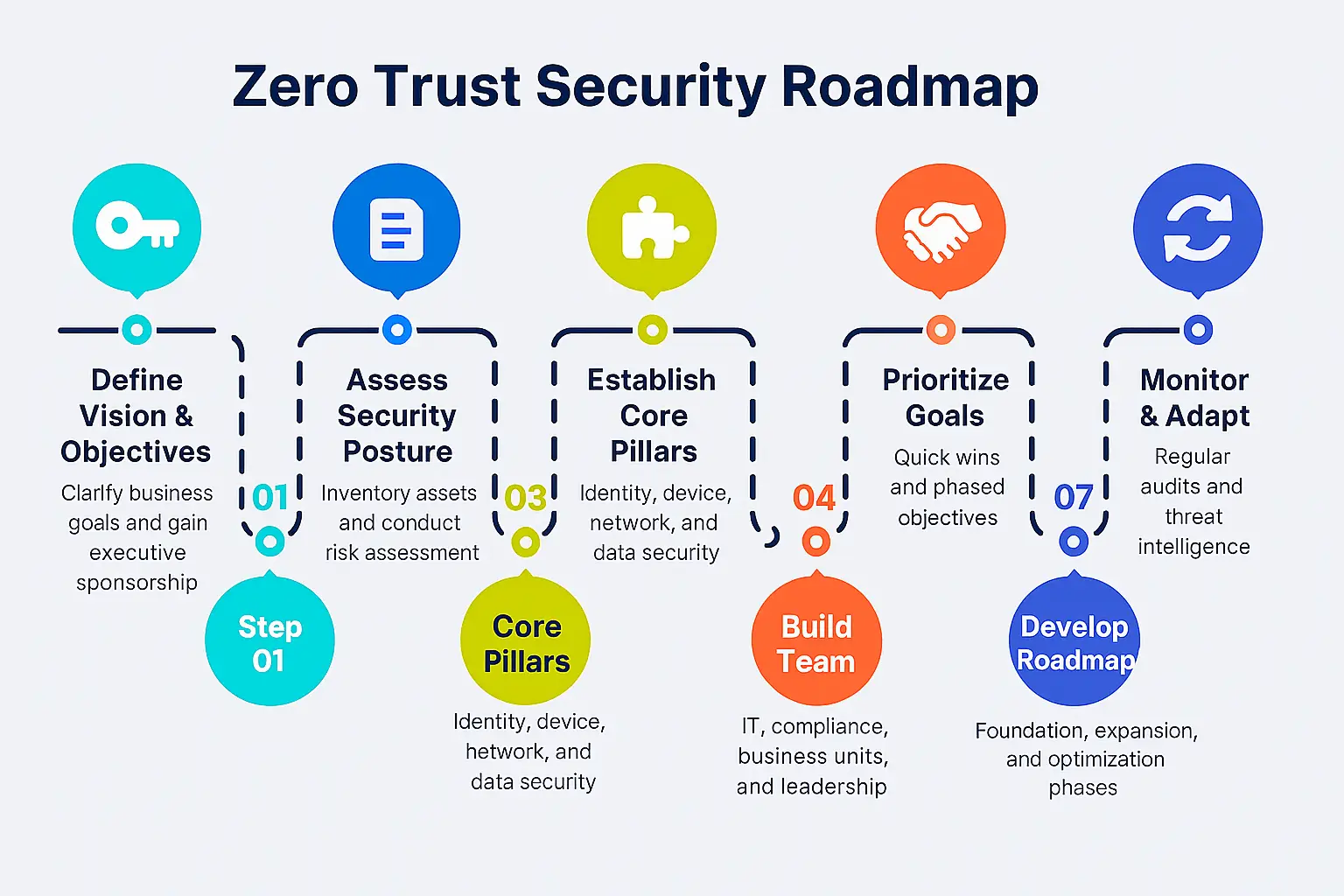
How to Implement This Security Model
Adopting a trust-based access approach is a journey, not a one-time project. Here’s how to get started:
- Assess your current security posture
- Identify critical assets and data
- Map out user roles and access needs
- Implement strong identity verification (IAM and IGA Identity Data Quality)
- Segment your network and apply least privilege (Effective Network Segmentation Strategies for Corporate Networks)
- Monitor continuously and refine policies (5 Reasons Continuous Threat Exposure Management Matters Today)
Step-by-step guides:
- How To approach implementing Zero Trust?
- Advice – Prepare a Zero Trust Roadmap
- Zero Trust Implementation Guide (OLOID)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Zero Trust security?
-
This framework requires all users and devices to be authenticated and authorised, regardless of their location.
Understanding Zero Trust Maturity Models: We Compare the 3 Main Approaches
CISA: What is Zero Trust? - How does it differ from traditional security models?
-
Traditional models trust users inside the network by default. This approach assumes no implicit trust and verifies every access request.
How to Measure Zero Trust Maturity: Practical Steps, Common Gaps, and Implementation Guide
NIST Zero Trust Architecture (SP 800-207) - What are the main benefits?
-
This model reduces the risk of breaches, improves compliance, and provides greater visibility and control over your IT environment.
Search our Latest Insights
Forrester: Zero Trust Security Business Benefits
The Future of Trust-Based Security
As cyber threats continue to evolve, this approach is set to become the default security model for organisations worldwide. It’s not just about technology—it’s about changing how we think about trust, access, and risk.
Further reading: